Discover Classical & Traditional Painting: Realism & Harmony
Classical and traditional painting styles refer to the methods and approaches that emphasize realism, proportion, symmetry, and balance. These styles are deeply rooted in the art traditions of ancient civilizations, particularly those of Greece and Rome, and they have been carried forward through various periods of history, such as the Renaissance, Baroque, and Neoclassicism.
Key Characteristics of Classical and Traditional Painting
- Realism:
- The focus is on accurately depicting the human form, objects, and the natural world as they appear to the eye. Artists aim for precision, capturing fine details and lifelike appearances.
- Artists carefully study anatomy, light, and perspective to create works that look as realistic and accurate as possible.
- Proportion and Symmetry:
- Classical art emphasizes mathematical precision, especially in the proportions of the human body. This is evident in works such as Leonardo da Vinci’s Vitruvian Man, which showcases the ideal human proportions.
- Symmetry, balance, and harmony are important in the composition of the artwork.
- Use of Light and Shadow (Chiaroscuro):
- Classical painters often used light and shadow to create a sense of depth and volume. This technique, known as chiaroscuro, helps give figures and objects a three-dimensional quality.
- Dramatic contrasts of light and dark were later perfected during the Baroque period.
- Focus on Mythology, History, and Religion:
- Classical painting often depicts themes from mythology, history, and religious texts. The subjects are often noble, heroic, or divine figures drawn from ancient stories or the Bible.
- Perspective and Depth:
- Artists use techniques like linear perspective, where parallel lines converge at a vanishing point, to create the illusion of depth in a two-dimensional space.
- Atmospheric perspective, where colors and details fade as they recede into the distance, adds to the sense of realism.
- Idealization:
- Rather than showing the flaws or imperfections of people and objects, classical art often idealizes them, portraying beauty and perfection. The goal is to present a harmonious, elevated view of the world.
- This idealization is particularly evident in depictions of the human body, which is often shown as perfectly proportioned and elegant.
Classical and traditional painting styles prioritize realism, order, and harmony, often using techniques that emphasize balance, depth, and ideal beauty. These styles continue to influence many forms of contemporary art today.
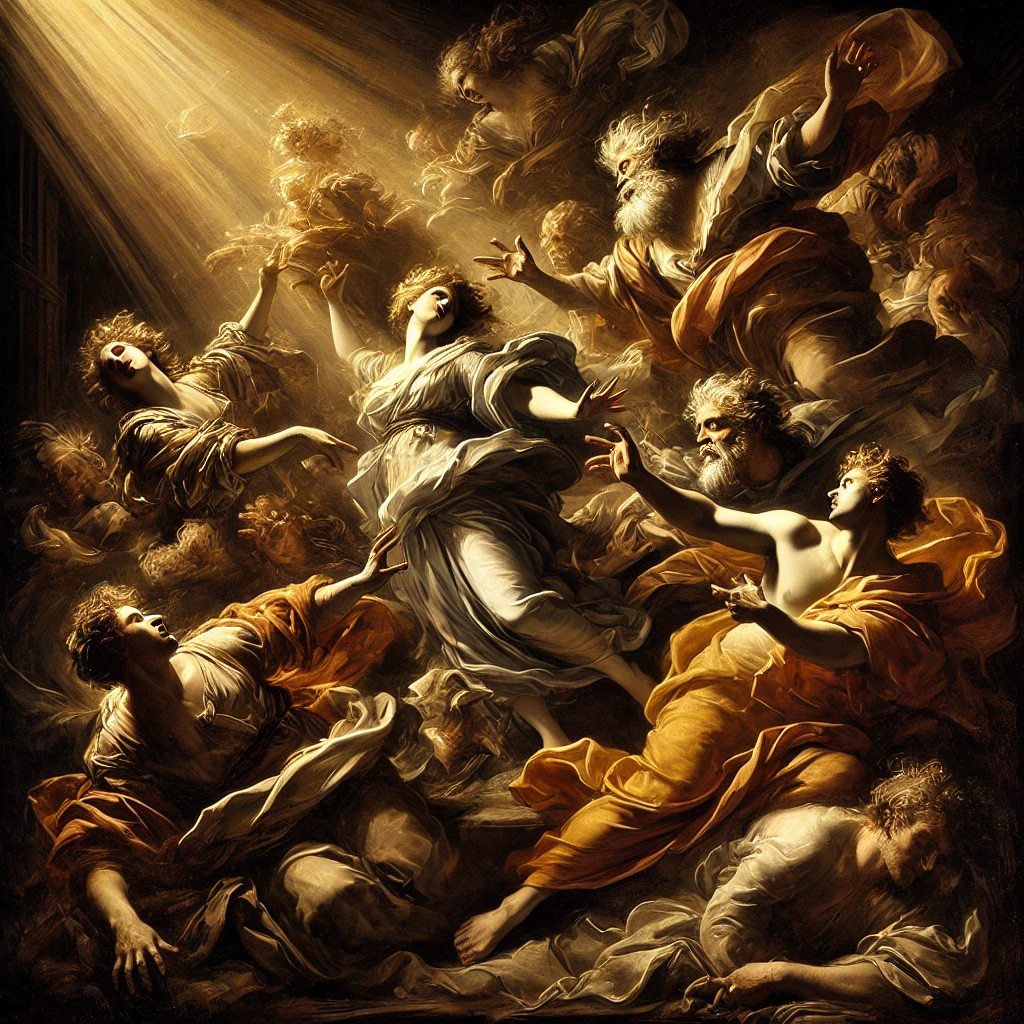

Baroque
Baroque dramatic use of light and shadow, vivid color, and intense emotional expression (e.g., Caravaggio, Rembrandt).
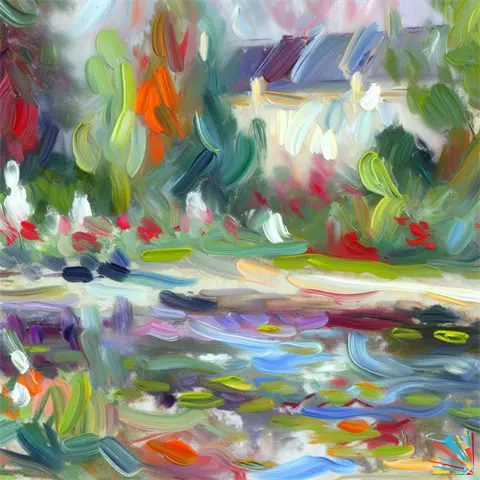
Impressionism
Impressionism is characterized by visible brush strokes, emphasis on light and its changing qualities, often painted outdoors (e.g., Monet, Renoir).
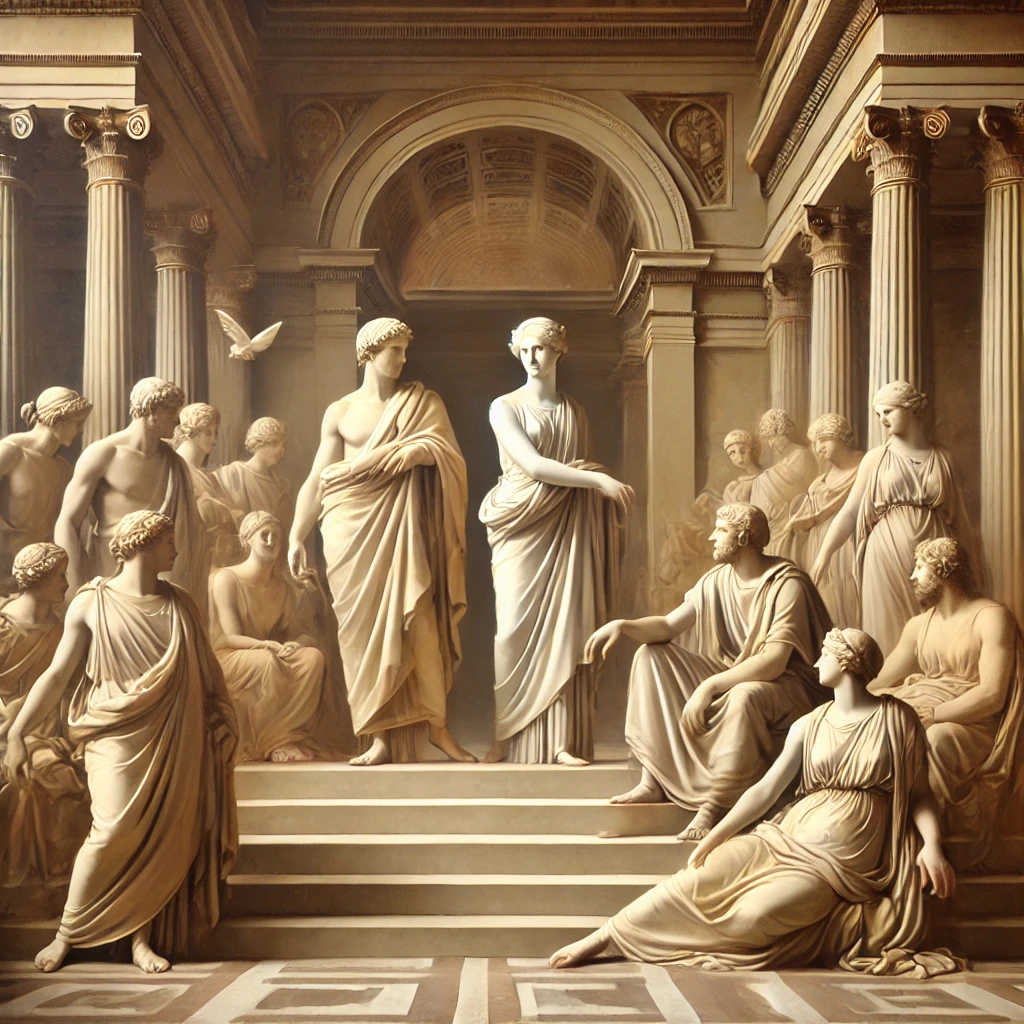

Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism draws inspiration from the classical art and culture of Ancient Greece and Rome, with an emphasis on order and symmetry.

Pointillism
Pointillism uses small, distinct dots of color applied in patterns to form an image (e.g., Georges Seurat).
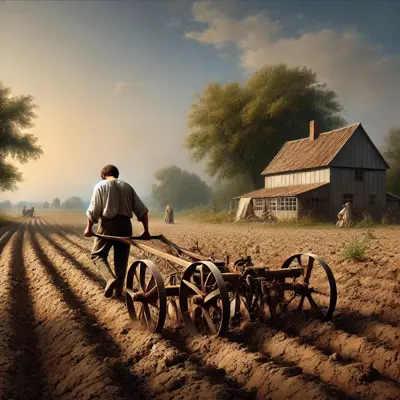

Realism
Realism focuses on depicting subjects as they appear in everyday life, with accurate, detailed representation.
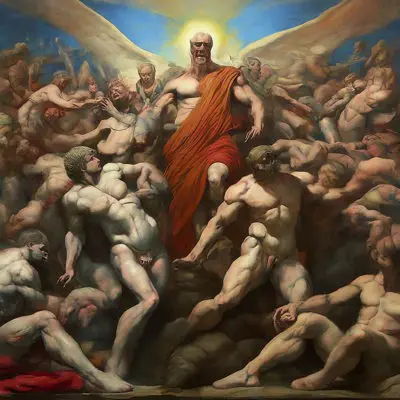

Renaissance
Renaissance revived interest in classical antiquity, focusing on proportion, perspective, and human anatomy (e.g., Michelangelo, Raphael).
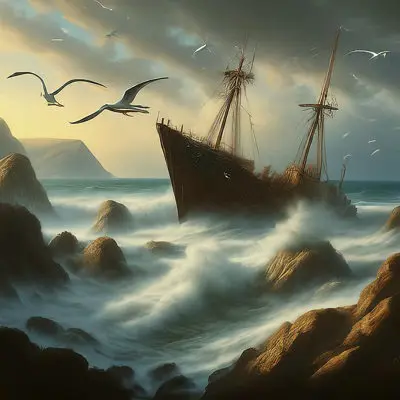

Romanticism
Romanticism focuses on emotion, individualism, and the glorification of nature, often with dramatic scenes (e.g., Turner, Delacroix).
